|
21.01.2008
Describing an alternative method to FTP over TLS by the use of WebDav over TLS published through ISA 2006 Firewall - Part 5 - Configure HTTP Filtering in ISA 2006 Firewall
ISA 2006 Firewall can provide granular control over HTTP traffic through the HTTP filter, an application-layer filter that examines HTTP commands and data.
The HTTP filter screens all HTTP traffic that passes through the ISA Server computer, and only allows compliant requests to pass through. This significantly improves the security of your Web servers, by helping ensure that they only respond to valid requests.
Let's take a quick look at it regarding the scenario from this article.
You can find out more about HTTP filtering in ISA by reading the following Microsoft docs:
- HTTP Filtering in ISA Server 2004
- Typical HTTP Policies for Web and Outlook Web Access Publishing Rules
- HTTP Policy Walk-through Procedure 2: Configure HTTP Policy
And from this article written by Marc Grote: Configuring the ISA Server 2006 HTTP Filter
You can configure the HTTP filter by right-click on the WebDav Web Publishing rule and "Configure HTTP". See Figure103.
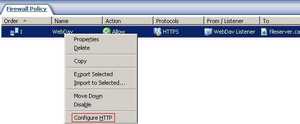
Figure103: Configure HTTP
And you can start configuring the HTTP policy for this rule. See Figure104, General tab.
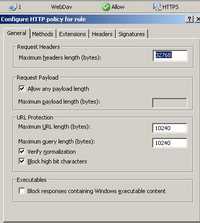
Figure104: HTTP Filter General tab
The "Verify Normalization" or "Block high bit characters" features did not block access to my WebDav server using the various WebDav clients presented in this article. However "Block high bit characters" might interfere if you are using a language containing high-bit characters. "Verify Normalization" blocks requests with URLs containing escaped characters after normalization.
Note that the "Maximum headers length" setting on the General tab of the Configure HTTP policy for rule dialog box is applied to all rules globally, so if you change it here it will apply to all rules.
You can also type the maximum URL length allowed. You enter that value in bytes. Requests with URLs exceeding this value will be blocked. See Figure105.
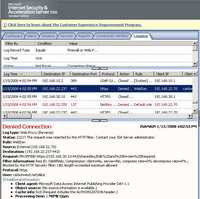
Figure105: HTTP Filter General
For example I have considered that a maximum URL length of 120 bytes is enough for the WebDav web publishing rule used within this article (obvioulsy I've double-checked that). See Figure106.
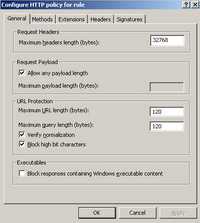
Figure106: Maximum URL Length
Also you can check "Block responses containing Windows executable content" which allows you to prevent users from downloading files that are Windows executable. The HTTP filter knows if the file is a Windows executable because the response will begin with " MZ".
Click the "Methods" tab. See Figure107.
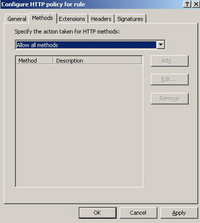
Figure107: Configure HTTP Methods Tab
Here you have the choice of blocking some Methods or allow only some Methods. This is very useful for our webDav server.
First let's talk about some of the methods that might be used within the scenario of this article(see RFC2068, RFC2518 and RFC4918 for more details).
- OPTIONS Method represents a request for information about the communication options available on the request/response chain identified by the Request-URI. This method allows the client to determine the options and/or requirements associated with a resource, or the capabilities of a server. See Figure108.
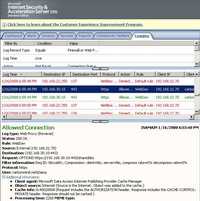
Figure108: OPTIONS Method ISA Log
- PROPFIND Method retrieves properties defined on the resource identified by the Request URI or on the resource identified by the Request URI and potentially its member resources, if the resource is a collection that has internal member URLs. The PROPFIND Method can be used on collection and property resources. The PROPFIND method can be used to list all the files in the DAV-enabled directory. WebDAV clients retrieve properties of documents using the PROPFIND method. See Figure109.
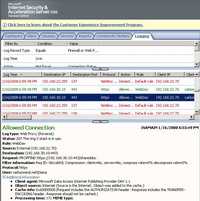
Figure109: PROPFIND Method ISA Log
- PROPPATCH Method processes instructions specified in the request body to set and/or remove properties defined on the resource identified by the Request-URI. WebDAV clients assign properties to documents using the PROPPATCH method. Can be used to set properties for the resource at the specified destination URI. Figure110 shows the ISA Log for the operation of creating a new .txt file on the WebDav server using WebDrive.
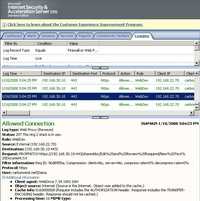
Figure110: PROPPATCH Method ISA Log
- GET Method means retrieve whatever information. It specifies that a resource is being retrieved from the server. From an end-user point of view this might be associated with the download process. See Figure111.
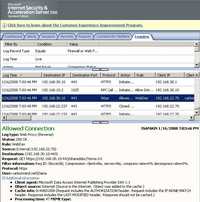
Figure111: GET Method ISA Log
- HEAD Method is used to ask for information about a document. Is identical to GET except that the server MUST NOT return a message-body in the response. HEAD is much faster than GET, as a much smaller amount of data is transferred. It's often used by clients who use caching, to see if the document has changed since it was last accessed. If it was not, the local copy can be reused, otherwise the updated version must be retrieved with a GET. As said before, this method is often used for testing hypertext links for validity, accessibility, and recent modification. See Figure112.
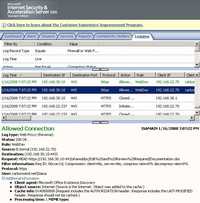
Figure112: HEAD Method ISA Log
- PUT Method requests that the enclosed entity be stored under the supplied Request URI. If the Request URI refers to an already existing resource, the enclosed entity should be considered as a modified version of the one residing on the origin server. If the Request URI does not point to an existing resource, and that URI is capable of being defined as a new resource by the requesting user agent, the origin server can create the resource with that URI. From an end-user point of view is tipically associated with the upload process(uploading a new file or updating an old one). See Figure113.
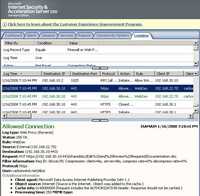
Figure113: PUT Method ISA Log
- DELETE Method requests that the origin server deletes the resource identified by the Request URI. From an end-user point of view is tipically associated with the delete process(the user deletes a file or a directory on the remote server). See Figure114.
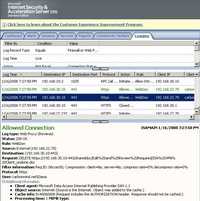
Figure114: DELETE Method ISA Log
- MOVE Method applied on a non-collection resource is the logical equivalent of a copy (COPY Method), followed by consistency maintenance processing, followed by a delete of the source, where all three actions are performed atomically. From an end-user point of view can be associated with the rename process(the user renames a file or directory on the remote server). See Figure115.
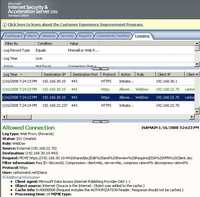
Figure115: MOVE Method ISA Log
- COPY Method creates a duplicate of the source resource, identified by the Request-URI, in the destination resource, identified by the URI in the Destination header. The Destination header must be present. The exact behavior of the COPY method depends on the type of the source resource. From an end-user point of view it can be associated with the action of Copy and Paste of a file for example, directly on the remote directory thus creating a duplicate of that file. See Figure116 and Figure117.
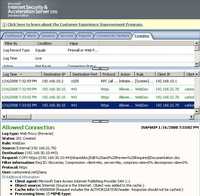
Figure116: COPY Method ISA Log
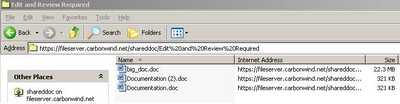
Figure117: Duplicate File
- LOCK Method is used to put a lock on a resource. Locks a document(example Word doc) so other users can't edit it. This assures overwrite prevention. One user edits the document while the rest of the users can read it. See Figure118.
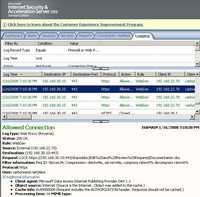
Figure118: LOCK Method ISA Log
- UNLOCK Method is used to remove a lock from a resource. Unlocks the document previously locked. Typically this happens when the user closes the document(example Word doc). See Figure119.
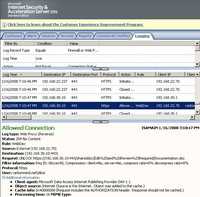
Figure119: UNLOCK Method ISA Log
- MKCOL Method creates a new collection at the location specified by the Request URI. It can be used for creating new folders for example on the remote WebDav server. See Figure120.
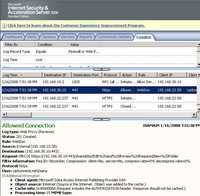
Figure120: MKCOL Method ISA Log
If you want your users to be able to do all the things described by the above methods then you should configure them as allowed methods on ISA. See Figure121.
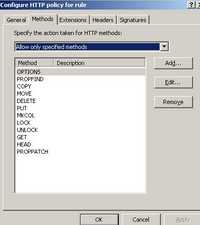
Figure121: Allowed Methods
Click the Extensions tab. See Figure122.
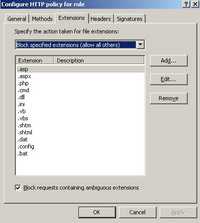
Figure122: The Extensions Tab Blocked Extensions
Here you have the choice of blocking file extensions or allowing only needed extensions. I have quickly configured a few blocked extensions. This may vary depending on what you plan to allow/block to be uploaded or downloaded from your server.
Also you can select "Block requests containing ambiguous extensions", thus requests whose file extension cannot be determined will be blocked.
It will be more secure for your WebDav server to allow only needed extensions(depending on what types of files you store on the WebDav server). See Figure123.
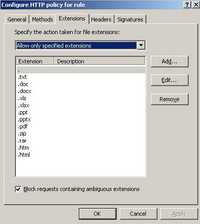
Figure123: The Extensions Tab Allow Only Specified Extensions
Please note that if you change the extensions of a file from .jpg to .zip ISA will not block the upload of this "new" file, only the extension matters, ISA does not verify the file. Also the "." extension is needed otherwise you will not be able to connect(for example a request for https://fileserver.carbonwind.net/shareddoc will be denied). See Figure124.
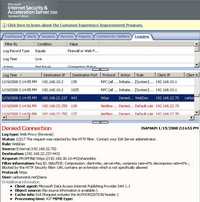
Figure124: ISA Log Extension Not Specifically Allowed
Click the Headers tab. See Figure125.
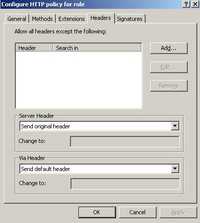
Figure125: The Headers Tab
You can block certain headers(response, request). You can also specify how the server header will be returned in the response.
I've made no changes to this tab.
Click on the signatures tab. See Figure126.
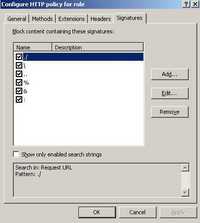
Figure126: The Signatures Tab
Here you can specify whether requests or responses will be blocked based on the presence of specific signatures in the headers or body or Request URL.
I have entered a quick list of signatures for the Request URL. If any of these strings will be found in the Request URL, the request will be blocked.
As can be seen, using the HTTP filter you can go a long way in protecting your WebDav server.
For example imagine that you want to allow two types of access: for power users(like above allow these users to read, delete, rename or edit files) and for normal users(they are only allowed to read and download files). Even more, you want the normal users to have access only to the a specific directory on the WebDav server (like a folder with public docs).
ISA 2006 Firewall enables you to control all these at the firewall level. Therefore the unwanted normal users requests will never reach the WebDav server behind ISA.
Right-click the WebDav publishing rule and click Copy. See Figure127.
Figure127: Copy Rule
Then one more time right-click that rule and click Paste. See Figure128.
Figure128: Paste Rule
And a new Web Publishing rule named WebDav(1) appears. See Figure129.
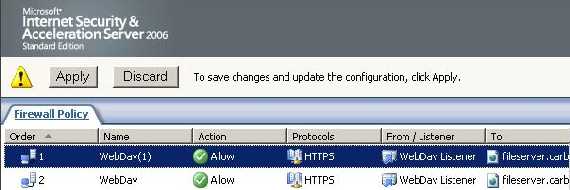
Figure129: New Web Publishing Rule
Do not commit yet your changes.
Right-click it and click Properties. Click the Paths tab. And edit the path to be "/shareddoc/PublicDoc/*" instead of "/shareddoc/*". See Figure130.
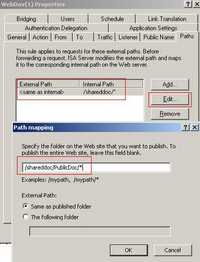
Figure130: WebDav(1) Path
Next click the Users tab and remove the "WebDav Users" group and add the new users group. I've called this group "WebDav2" Users which corresponds to the "WebDav2" Windows Group. See Figure131.
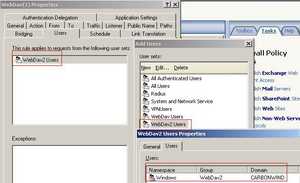
Figure131: WebDav2 Users
Click OK to close WebDav(1) properties.
Then right-click the WebDav(1) rule and click Configure HTTP Filter. See Figure132.
_ConfigureHTTP.JPG)
Figure132: WebDav(1) Configure HTTP
Click the Methods tab. Allow only "OPTIONS", "PROPFIND", "GET" and "HEAD" (remove the rest). See Figure133.
_Methods.jpg)
Figure133: WebDav(1) Methods Tab
Doing so "WebDav2 Users" will only be able to read, list, browse and download files.
Click "OK" and apply the new settings.
And the normal users are able to connect to the PublicDoc directory. See Figure134.
.jpg)
Figure134: PublicDoc WebDav(1)
ISA allows the PROPFIND method for the WebDav2 user. See Figure135.
.jpg)
Figure135: ISA Log PROPFIND WebDav(1)
A WebDav2 user attempts to download a file. The request is allowed by ISA. See Figure136.
.jpg)
Figure136: ISA Log GET WebDav(1)
If the WebDav2 user wants to upload a file, ISA denies him. See Figure137.
.jpg)
Figure137: ISA Log PUT WebDav(1)
Also if WebDav2 user attempts to enter the SharedDoc directory ISA denies him. See Figure138.
.jpg)
Figure138: ISA Log Denied Action
So the two rules are doing their job. See Figure139.
Figure139: The Two Rules in Action
As we have seen throughout this series, the described method gives us a very nice FTPS like solution while we are able take advantage of ISA's powerful features.
In Part 6 we will discuss the use of a user certificate as a strong authentication method(high security) instead of the user/password method.
|