Yep, the future version of ISA, TMG, will provide SSL VPN through SSTP(using RRAS).
SSL VPN was a highly missed feature from ISA Server 2004/2006.
TMG, through SSTP offers full VPN access, and not just a browser-based VPN(sometimes labeled as clienteles SSL VPN, although in order to provide “full network access”, this clientless approach will require a “program” to be loaded on client computer). Currently you can use the built-in SSTP VPN clients from Windows Vista and Windows 7 RC to connect to the TMG Beta 3 SSTP VPN server.
As with ISA Server 2004/2006 and PPTP and L2TP/IPsec VPN connections, you can use the same granular access rules to provide per user/group access to resources for SSTP remote access VPN connections on TMG Beta 3(even for clients using EAP-based user authentication methods).
And now TMG comes with NAP support, so you can check the health status of the SSTP|L2TP/IPsec|PPTP VPN clients.
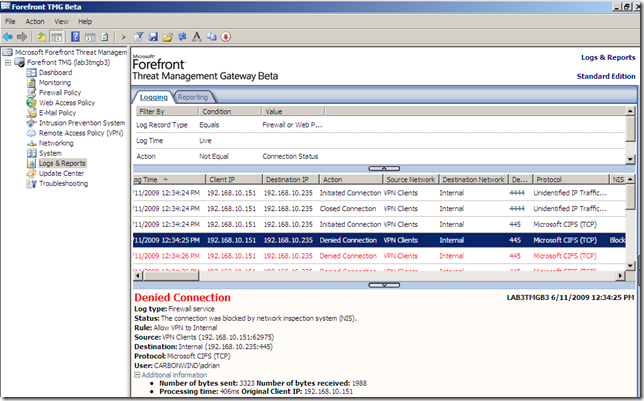
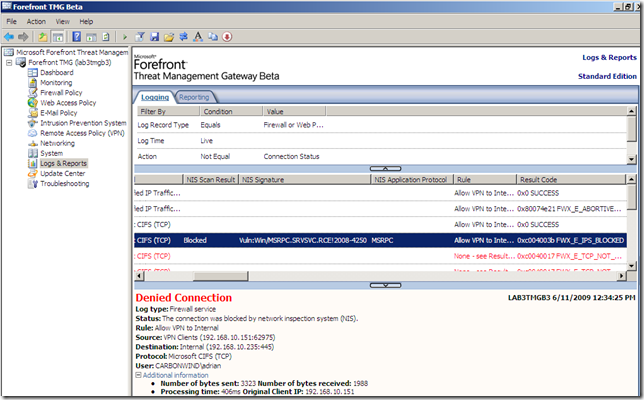
Also the IPS inspects the VPN clients’ traffic(see bellow for details).
So it seems that TMG will provide a more robust remote VPN access solution than its predecessor ISA Server.
Let’s take a quick look at the SSTP VPN on TMG Beta 3:
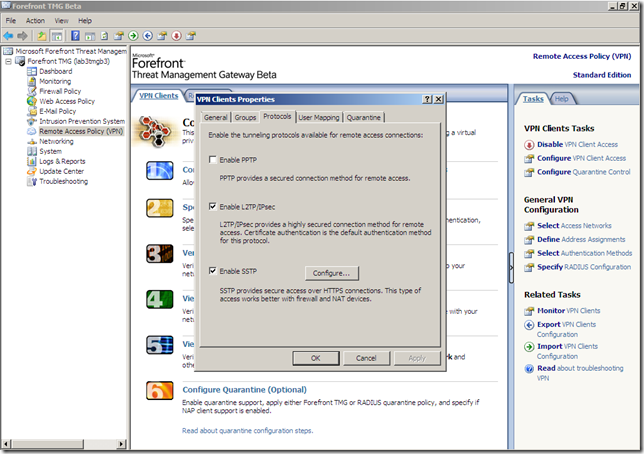
If you are familiar with Windows Server 2008’s RRAS and SSTP, you will be pleasantly surprised by the ingenious solution used on TMG Beta 3 to specify the IP address and the certificate used by the SSTP VPN server: configuring a web listener(in a simplified form):
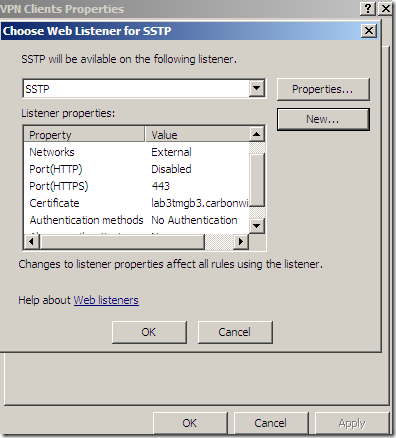
Let’s see a little bit this web listener:
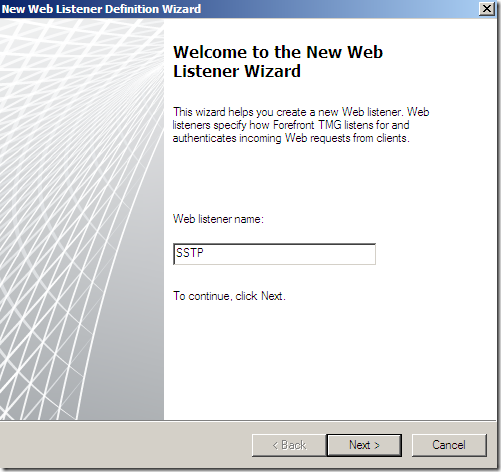
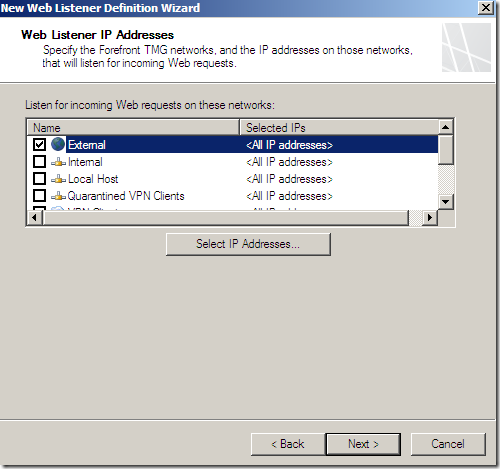
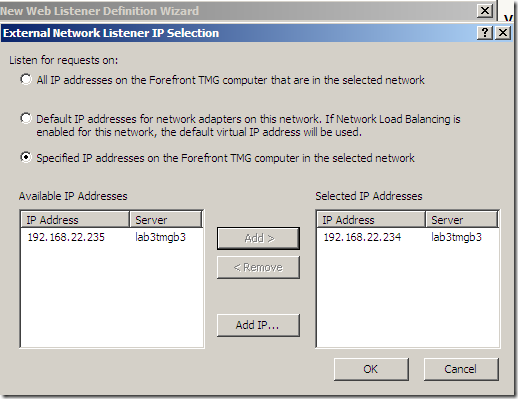
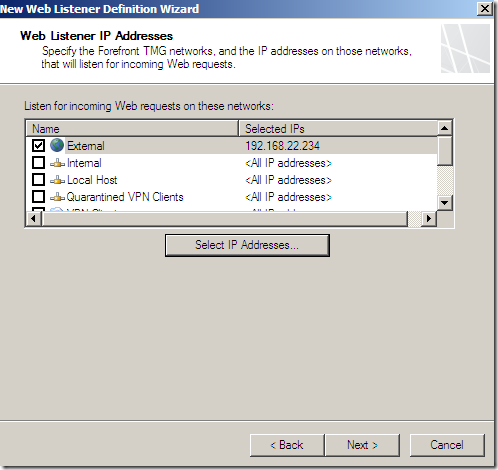
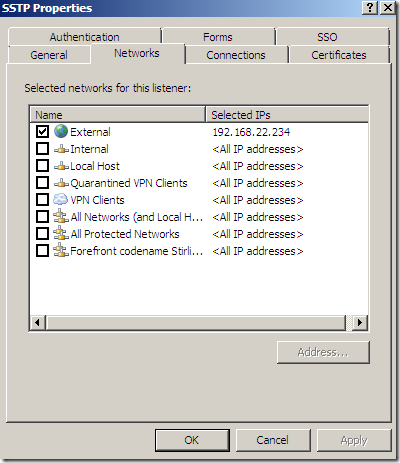
Specify the IP address on which TMG will listen for incoming SSTP VPN connections:
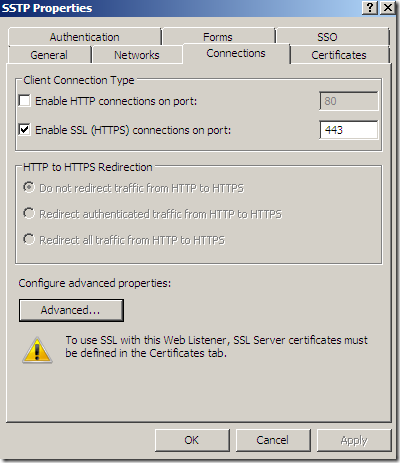
Specify the certificate to be used for SSTP:
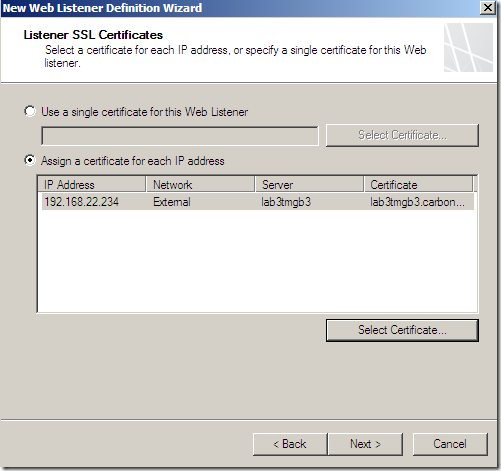
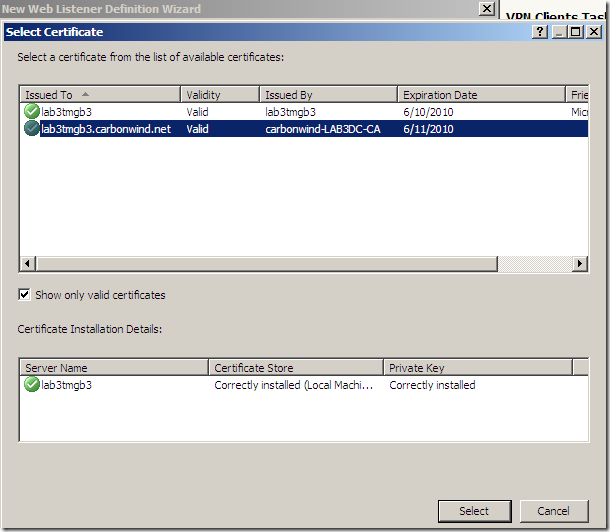
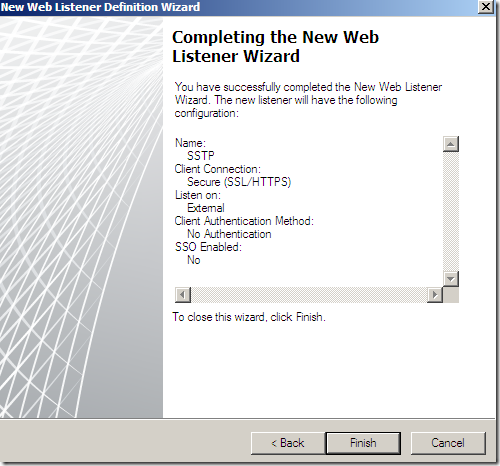
And that’s it:
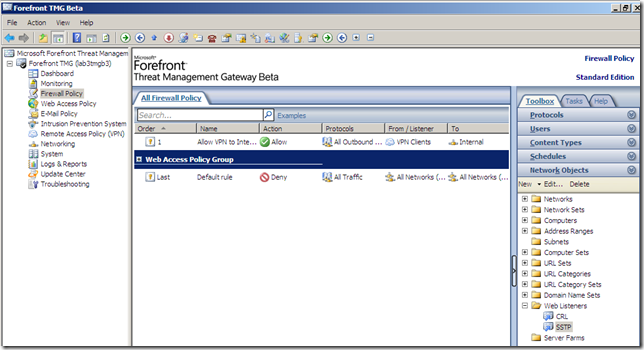
You can spot the created web listener if you head over to the Firewall Policy node, Toolbox panel, Network Objects/Web Listeners(but perhaps you should not try to modify it from there):
As already said, you can use NAP with SSTP, if you want.
Full access when the VPN client passes the health checks:
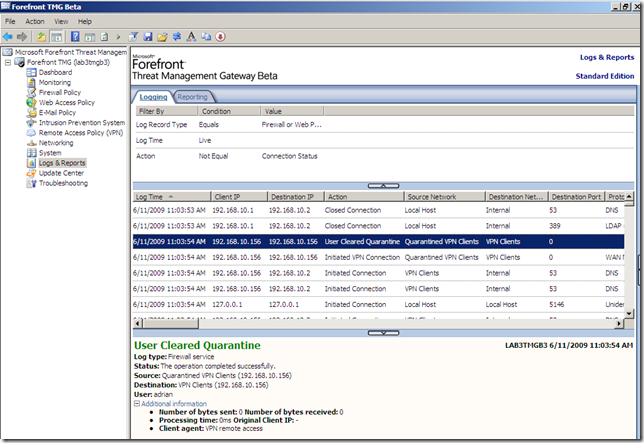
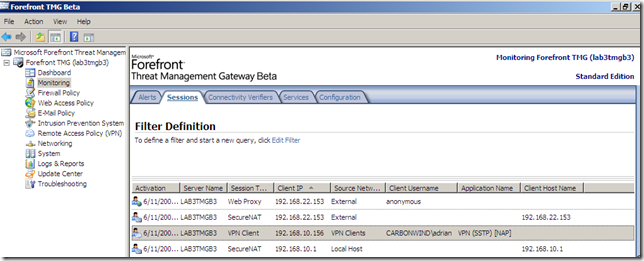
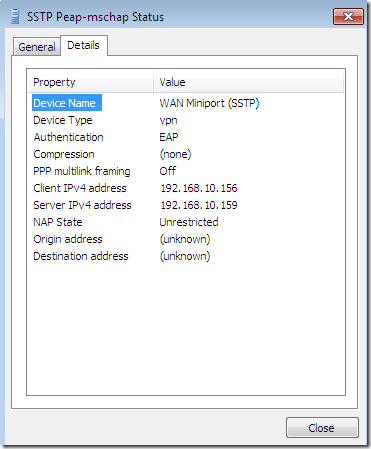
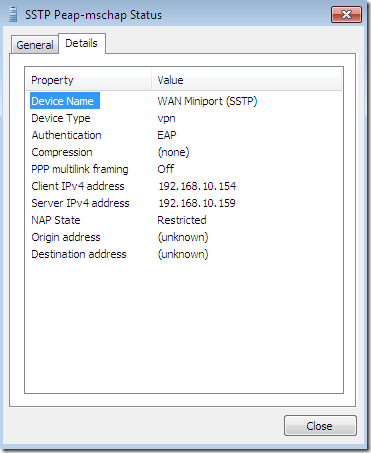
Restricted access due to non-compliance:
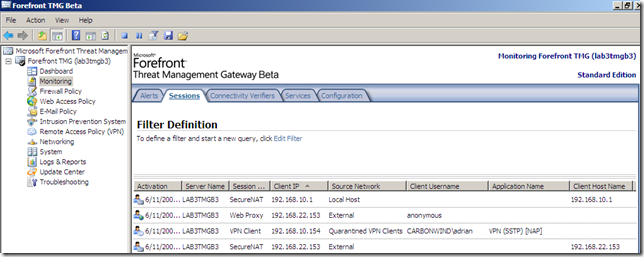
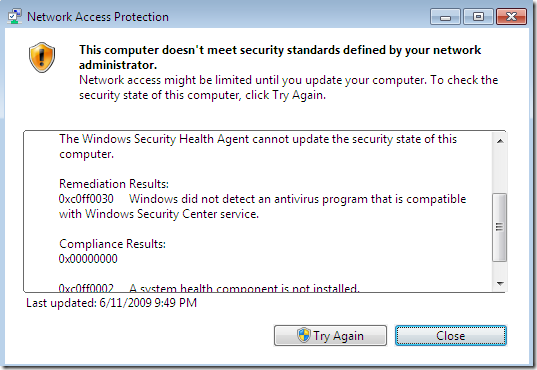
IPS in action, a VPN client tries to compromise a file sharing server behind the TMG Beta 3 VPN server by attempting to exploit a vulnerability: